What is gabion?
Gabion is a welded wire cage or box filled with materials such as stone, concrete, sand, or soil. So, the gabion is a partially flexible block construction used for slope stability and erosion protection in construction. Various types of gabions are constructed and used in different engineering constructions.Sometimes, live rooting branches may be placed between the rock-filled baskets which improve the durability and stability of the gabion. This article presents a gabion definition, types, applications, and advantages.
Gabion wire mesh properties
Wire mesh used to manufacture the cage of gabion shall pose certain properties otherwise it might not serve its purpose properly. Table 1 provides the desired properties of the gabion wire mesh.
Table-1: Gabion wire mesh properties
Raw material Gabion wire mesh properties
Technical properties Unit Descriptions Tolerances
Mesh mm 50×70, 60×80, 80×100, and 100×120 —
Maximum wire thickness mm 2-5 0.05
Amount of covering gr/m2 30-300 5
Tensile strength MPa 350-2000 2
Elongation (25cm long) — 10% —
Zinc coating strength Turns 5 Shall not break or crack
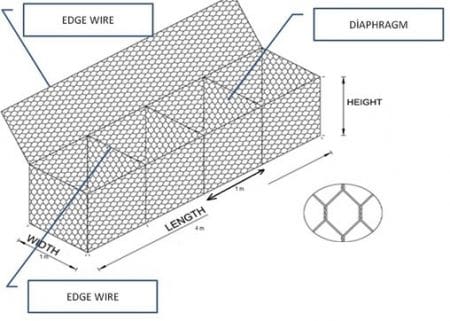
Fig. 1: Wire mesh boxes for gabions
1. Gabion baskets
It is a net wire mesh that produced in box-shaped and in different sizes.
Used in highway and railway works.
It would be economical unless filling materials are not available from quarries near the project site.

Fig.2: Basket gabion
Technical properties Unit Descriptions Tolerances
Mesh mm 50×70, 60×80, 80×100, and 100×120 —
Maximum wire thickness mm 2-5 0.05
Amount of covering gr/m2 30-300 5
Tensile strength MPa 350-2000 2
Elongation (25cm long) — 10% —
Zinc coating strength Turns 5 Shall not break or crack

Fig. 1: Wire mesh boxes for gabions
Types of Gabions
There is a number of gabion configurations that can be selected based on their cost and function. Common types of Gabion are as follows:1. Gabion baskets
It is a net wire mesh that produced in box-shaped and in different sizes.
Used in highway and railway works.
It would be economical unless filling materials are not available from quarries near the project site.

Fig.2: Basket gabion
2. Gabion mattresses
Gabion mattresses, also known as reno mattresses.
Gabion mattresses, also known as reno mattresses.
Gabion mattress's height is shorter than the other types of measurements as it might be observed from Fig. 3.
It is employed in the channel coating for preventing erosion. So, it tackles wave and erosion induced velocity.
The common size, 6 m long by 2 m wide by 0,3 m high.

Fig. 3: Gabion mattress
It is employed in the channel coating for preventing erosion. So, it tackles wave and erosion induced velocity.
The common size, 6 m long by 2 m wide by 0,3 m high.

Fig. 3: Gabion mattress
3. Gabion sacks
This type of gabions is formed quickly.
It has a porous and flexible structure.
Gabion sacks are usually used in hydraulic works in emergency conditions.

Fig. 4: Gabion sacks
This type of gabions is formed quickly.
It has a porous and flexible structure.
Gabion sacks are usually used in hydraulic works in emergency conditions.

Fig. 4: Gabion sacks
4. Gabion wire mesh
It is utilized to keep the possible rock and stone fall on the highway and railway surfaces.
Gabion wire mesh maintains the stability of the slope close to the highway and railways.
It is applied for anti-erosion to the slope.
It enhances embankment soil strength in combination with geogrid reinforcement.

Fig. 5: Gabion wire mesh used to prevent rockfall from highway slopes
5. Decorative Gabion Elements
It is used indoor and outdoor decoration, garden design and landscaping.
Gabion elements offer a suitable environment for the growth of plant roots

Fig. 6: Decorative gabion elements
Retaining structures such as retaining walls (Fig. 7), revetment and toe walls to embankments and cuttings.
Corrosion prevention structures, for instance, sea walls, riverbank defenses, canal banks (Fig. 8), dams, weirs, groins and for the protection of reservoirs and lakesides.
cylindrical metal gabion is used for dams or in foundation construction.
It is employed as a noise barrier.
Gabions are also used as temporary floodwalls.
It is utilized to change the direction of the force of floodwater around the weak structure
Stepped gabions improve energy dissipation in channels.
Finally, it is used for aesthetic purposes

Fig. 7: Gabion retaining wall for road embankment

Fig. 8: Gabion mattresses used for covering channels to prevent erosion

Fig. 9: Use of gabions in landscaping

Fig. 10: Gabions used for aesthetic purpose
Gabion has a very high resistance to atmospheric corrosion because of the well-bonded zinc coating on the wire and its ability to support vegetation growth.
2. Flexibility
This feature permits the gabion to settle and deform without failure and loss of efficiency. Specifically, when unstable ground and moving water are encountered.
3. Permeability
It provides automatic and easy drainage which eliminates the need for the installation of drainage pipes.
4. Strength
Gabions are satisfactory strong that is it is capable of resisting flood force, torrential force, and ice and earth pressure.
5. Economical
It is more economical in terms of both material and labor in comparison with other gabion alternatives.
6. Environmentally friendly
Recycled materials can be placed into the gabion cage. The gaps in the soil between filling materials allow the plantation to grow over time. Gabion elements are not affected by natural phenomena.
It is utilized to keep the possible rock and stone fall on the highway and railway surfaces.
Gabion wire mesh maintains the stability of the slope close to the highway and railways.
It is applied for anti-erosion to the slope.
It enhances embankment soil strength in combination with geogrid reinforcement.

Fig. 5: Gabion wire mesh used to prevent rockfall from highway slopes
5. Decorative Gabion Elements
It is used indoor and outdoor decoration, garden design and landscaping.
Gabion elements offer a suitable environment for the growth of plant roots

Fig. 6: Decorative gabion elements
Applications of gabions
Gabions are used in several engineering projects and serve various purposes. common applications of gabions are as follows:Retaining structures such as retaining walls (Fig. 7), revetment and toe walls to embankments and cuttings.
Corrosion prevention structures, for instance, sea walls, riverbank defenses, canal banks (Fig. 8), dams, weirs, groins and for the protection of reservoirs and lakesides.
cylindrical metal gabion is used for dams or in foundation construction.
It is employed as a noise barrier.
Gabions are also used as temporary floodwalls.
It is utilized to change the direction of the force of floodwater around the weak structure
Stepped gabions improve energy dissipation in channels.
Finally, it is used for aesthetic purposes

Fig. 7: Gabion retaining wall for road embankment

Fig. 8: Gabion mattresses used for covering channels to prevent erosion

Fig. 9: Use of gabions in landscaping

Fig. 10: Gabions used for aesthetic purpose
Advantages of gabions
1. DurabilityGabion has a very high resistance to atmospheric corrosion because of the well-bonded zinc coating on the wire and its ability to support vegetation growth.
2. Flexibility
This feature permits the gabion to settle and deform without failure and loss of efficiency. Specifically, when unstable ground and moving water are encountered.
3. Permeability
It provides automatic and easy drainage which eliminates the need for the installation of drainage pipes.
4. Strength
Gabions are satisfactory strong that is it is capable of resisting flood force, torrential force, and ice and earth pressure.
5. Economical
It is more economical in terms of both material and labor in comparison with other gabion alternatives.
6. Environmentally friendly
Recycled materials can be placed into the gabion cage. The gaps in the soil between filling materials allow the plantation to grow over time. Gabion elements are not affected by natural phenomena.
