Profometer test is a non-destructive testing technique used to detect the location and size of reinforcements and concrete cover quickly and accurately. A small, portable, and handy instrument which is known as profometer or rebar locator, is used in this test.
The equipment weight is less than two kgs, and works on normal batteries and thus does not require any electrical connection. The basic principle in this test method is that the presence of steel affects the electromagnetic field which is directed by profilometer device.
This instrument is available with sufficient memory to store measured data. Integrated software is loaded in the equipment for carrying out complicated calculations and printing statistical values.
Profilometer test is widely used and has many applications. For instance, it is used to specify reinforcement size, location, and condition of existing structures to evaluate their actual strength, location reinforcement is necessary to be determined prior to drilling and cutting cores for testing concrete, analysis of corrosion, conformity check, and quality assurance.
Purpose of Profometer Test
- Assess the location of steel bars
- Measure the diameter of reinforcement bars
- Evaluate the thickness of the concrete cover.
Principle of Profometer Test
The instrument is based upon measurement of the change of an electromagnetic field which is caused by steel bars embedded in the concrete.
Calibration of Profometer Equipment
Profometer device needs to be calibrated before starting the operations and at the end of the test in order to ensure satisfactory working and to get accurate results. To achieve this purpose, the test block provided with the instrument should be used.
To check the calibration accuracy, the size and cover of the reinforcement of the text block is measured at different locations by using profometer equipment.
Then compare the recorded data with the standard values prescribed on the test block. The recorded data and the standard values should match.

Test Preparations
There are certain preparations that are required to be done before the testing operation begins. For instance, it is essential to conduct a proper assessment of the structure before the test.
For this purpose, proper staging, ladder or a suspended platform may be provided. Before actual scanning, marking is done with chalk on the concrete surface by dividing it into panels of equal areas.
Profometer Test Procedures1. Determine Steel Bar Location
Path measuring device and spot probes are used together for path measurements and scanning of rebars. These are connected to profometer via cables and are moved on the concrete surface for scanning the rebars and measuring the spacing. As soon as the bar is located, it is displayed on the screen. Once the bar is located, it is marked on the concrete surface.
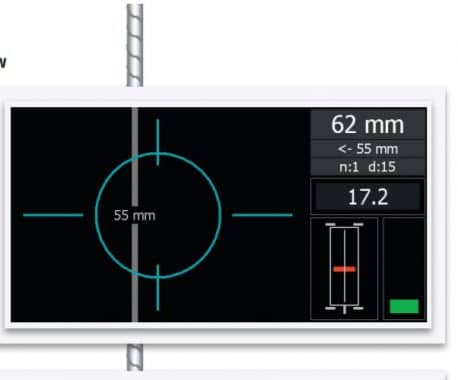
2. Measure Bar Diameter
The diameter probe is used for measuring the diameter of bars. It is also connected with profilometer by a cable. After finding out the location of rebar, the diameter probe is placed on the bar parallel to the bar axis. Four readings are displayed and the mean value of these readings is taken as the diameter of the bar.

3. Determine Concrete Cover
The depth probe of the profilometer is used to measure the cover. It is also connected with a profilometer by cable and is placed exactly on the bar. As soon as the depth probe is above rebar or nearest to it, it gives an audio signal through a short beep and visual display. Simultaneously, the measured concrete cover is stored in memory.
Precautions
There are various factors that affect Profometer results. These factors should be considered in the interpretation of observations obtained from this instrument:
- Arrangement of reinforcement,
- Variation in the iron content of cement and use of aggregate with magnetic properties,
- Metal ties also affect the magnetic field.
Advantages and Limitations
This is a purely non-destructive test for the evaluation of concrete structures, particularly old structures.
- The method is very fast and gives quite accurate results if the reinforcement is not heavily congested.
- The equipment is very light and even one person can perform the test without any assistance.
- Factors such as very closely spaced bars or bundled bars, binding wire, aggregate containing iron or magnetic properties would affect the accuracy of the measurements.
- Concrete cover thickness may be underestimated when special cement, including high alumna or added pigments, are used.
- Rebars in excess 32mm distance may require recalibration.
Applications
1.Evaluate the Strength of Concrete Structures
Profilometer test can be used to evaluate the actual strength of concrete structures in which the number of reinforcing bars, their condition of corrosion, concrete cover, and grade of concrete are required.
In the case of old structures, when the detailed drawings are not available, it becomes very difficult to compute the strength of the structure which is required for the strengthening scheme of the structure.
Sometimes, the strength of concrete structures is to be checked to permit higher load and in the absence of reinforcement details, it becomes very difficult to make a decision.
2. Corrosion analysis
3. The method can be used both for quality control as well as quality assurance of new structures.
4. Locating rebars is a necessity when drilling, cutting coring as well as a preliminary operation required for most other non-destructive investigations.













